We all care about our privacy, don’t we? It’s no longer optional to protect your online data in today’s world where everything is connected. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is the first thing you should use to protect your internet traffic. It makes a secure tunnel for it and keeps it safe from snoopers. But have you ever thought about how this magic really works? VPN protocols hold the key.
This detailed guide will look at the most common VPN protocols and talk about their pros and cons and when they are best used. By the end, you’ll not only know what VPN protocols are, but you’ll also be able to pick the best one for your needs. This is the place to go for all things related to “VPN Protocols Explained.”
What Are VPN Protocols, Exactly?
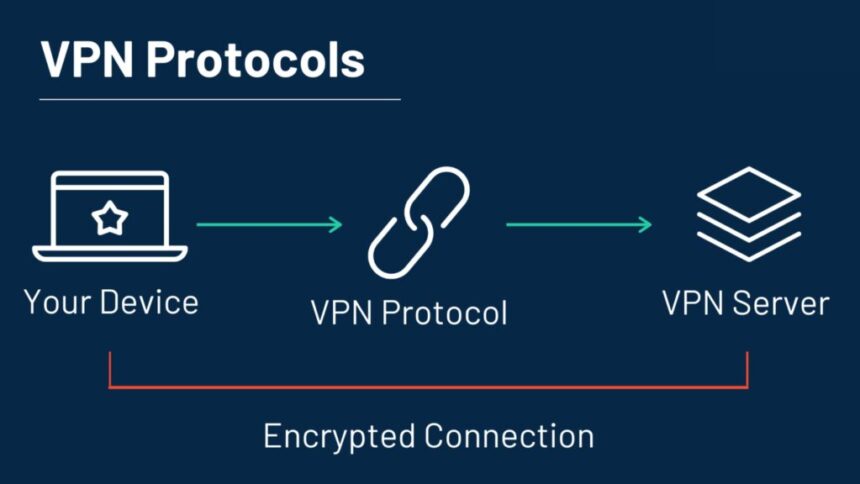
A VPN protocol is basically a set of rules or instructions that tell your device and the VPN server how to send data back and forth. You could say that this is the language your VPN connection speaks. It explains how the “tunnel” is made for your data to travel securely, how the encryption works, and how the authentication process works.
Different protocols use different ways to encrypt data, tunnel it, and speed it up, which means that they are not all equally secure, fast, or reliable. When choosing a VPN service and setting it up, it’s very important to know about these differences.
Picking the right VPN protocol is just as important for keeping your digital information safe as picking the right lock for your door. Some protocols put speed first, which makes them great for playing games or streaming 4K content. Others stress security that can’t be broken, which is very important when dealing with private or financial information. Some work better on mobile devices that switch networks a lot, while others work better on desktop computers with a stable connection. To make the right choice, you need to find a balance between your own needs for speed, safety, and stability.
The Main Players: A Close Look at Common VPN Protocols
Let’s look at the most popular VPN protocols and see what makes each one work. We’ll look at the technology, its pros and cons, and when you might want to use it.
OpenVPN: The Best of the Best
People often call OpenVPN the “gold standard” in the world of VPNs, and for good reason. It’s an open-source protocol, which means that cybersecurity experts all over the world can look at its code. This openness makes it easy to find and fix any security holes, which makes it very secure and always getting better through community audits.
Safety: OpenVPN is very strong. It works with strong encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with keys of different lengths (for example, 256 bits), which is the same standard that the U.S. government uses. It also uses digital certificates to prove who you are, which makes it very hard for hackers to listen in on conversations or steal data.
Flexibility: This is where OpenVPN really stands out. It can work with a number of transport protocols, but TCP and UDP are the most common.
OpenVPN TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): This method makes sure that data is sent in the right order and without errors. It checks for errors and sends any lost data packets again. This makes it very reliable, but it might make things a little slower. It’s great for browsing the web or sending emails where keeping data safe is very important.
OpenVPN UDP (User Datagram Protocol): This method puts speed ahead of making sure the message gets there. It sends data packets without checking that they all got there in the right order. This makes it a lot faster and perfect for things like streaming, gaming, and VoIP calls where speed is very important but a small packet loss isn’t a big deal.
Bypassing Firewalls: OpenVPN can run on any port, even TCP port 443, which is the default port for HTTPS traffic. This makes it very hard for firewalls to block it without also blocking secure web browsing. Because of this, it is a top choice for people who live in areas where the internet is heavily censored.
Platform Compatibility: OpenVPN works with a lot of different operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS) and devices, including many routers.
Best Use Cases: People who need strong security and dependability, especially when using public Wi-Fi, dealing with private data, or trying to get around strict firewalls.
Possible Drawbacks: It can be a little slower than newer protocols, especially when using the TCP configuration. Setting things up manually on some platforms without a provider’s app can be more difficult for beginners.
WireGuard: The New Kid on the Block
WireGuard is a fairly new protocol that has quickly become popular and is seen by many as the future of VPN technology. Its design philosophy is to be simple and work well.
Speed: WireGuard was made to be fast. Its modern design and efficient codebase (about 4,000 lines of code compared to OpenVPN’s hundreds of thousands) make connections much faster, with less lag, and connections happen much faster. This makes a big difference in how you use it every day.
Security: Don’t be fooled by the small codebase; WireGuard is very secure. It uses the most up-to-date cryptographic primitives, which are thought to be safer and more modern than some of the options available in older protocols. Its simplicity also makes it much easier for security experts to check, which makes it less likely that someone will attack it.
Platform Compatibility: WireGuard has grown very quickly, even though it is newer. It is now built right into the Linux kernel, and almost all major VPN providers support it on all major platforms (Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS).
Mobile Performance: It works great on mobile devices. It uses less battery power and handles changes to the network without any problems. When you switch from Wi-Fi to cellular data, it reconnects almost instantly.
Best Use Cases: People who want to do things like stream HD and 4K content, play games online, and download big files quickly and securely. It’s also the best option for people who use their phones.
Possible Problems: Because it is newer, it hasn’t been tested in the real world for as long as OpenVPN has. Early versions raised privacy concerns about how they logged IP addresses, but since then, trustworthy VPN providers have come up with effective workarounds, such as using a double NAT system, to fix this problem.
IKEv2/IPSec is quick and stable
Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) is a great way to make a secure connection. It almost always works with Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) to encrypt and verify the data. This mix is known for being fast, stable, and tough.
Speed and Stability: IKEv2/IPSec is usually faster than OpenVPN and very stable. The Mobility and Multihoming Protocol (MOBIKE) is what makes it special. It lets users keep their VPN connection even when they switch networks, like from a home Wi-Fi network to a mobile data network. This makes it very dependable for people who are always on the go.
Security: IPSec has a strong set of security protocols that are well-known. It works well with IKEv2 and modern encryption ciphers like AES-256 to provide strong security that businesses and governments around the world trust.
Platform Compatibility: It works on a lot of major operating systems, especially mobile ones like iOS and BlackBerry. This means you might not even need a third-party app to set it up (but it’s always best to use a provider’s app for ease of use and extra features).
Best Uses: People who use their phones a lot and switch between Wi-Fi and cellular data, business people who need a stable remote connection, and anyone who wants a fast and reliable connection.
Possible Drawbacks: Its use of UDP port 500 can make it easier for firewalls to block than OpenVPN running on TCP port 443, even though it is secure. Some privacy advocates may not trust it as much as open-source options because it is also a closed-source protocol.
L2TP/IPSec: A Good but Old Choice
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol that doesn’t encrypt anything by itself. Because of this, it is almost always used with the IPSec suite to keep things safe. It’s the next version of PPTP, which is no longer used.
Security: IPSec is the only thing that keeps L2TP safe. Some security experts are worried about IPSec because there are claims that the NSA purposely made it less secure.
Speed: It is usually slower than OpenVPN and WireGuard because it wraps data twice, which adds overhead and can slow down the connection.
Platform Compatibility: This protocol is very common and is built into almost all modern operating systems and devices that can connect to a VPN.
Best Uses: This is mostly used as a backup plan when newer, better protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard aren’t available or are blocked on a certain network.
Possible Drawbacks: The security profile isn’t as strong as OpenVPN and WireGuard, the speeds are slower, and it uses fixed ports that firewalls can easily block. People usually think of it as an old protocol.
PPTP: Don’t use it if you can help it
Microsoft made Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) in the 1990s. It is one of the oldest VPN protocols. It is simple to set up and very quick, but it has a lot of serious, well-known security holes.
Security: The security of PPTP is fundamentally broken. Its encryption methods are old and can be broken quickly and easily with tools that are easy to find. It shouldn’t be thought of as safe for anything.
Speed: Its only “advantage” is how fast it is, which is because its encryption is so weak.
Platform Compatibility: Most well-known VPN providers have stopped using it because of security issues, but it is still widely supported.
Best Uses: To be honest, none. PPTP is not the best choice for any modern situation because it has serious security flaws. It gives you a false sense of safety.
Possible Problems: It has major security holes that can’t be fixed, so it can’t be used to protect any kind of data.
Useful Tips for Picking and Using the Right VPN Protocol
Now that you know more about the different VPN protocols, let’s talk about how to use this information in your daily life.
Put Security First: If your main goal is to keep your online identity, banking information, or private data safe, always choose OpenVPN or WireGuard. These protocols have the best encryption and are checked for weaknesses on a regular basis.
Optimize for Speed: If you need high bandwidth and low latency for things like streaming 4K movies, playing competitive online games, or video conferencing, WireGuard is usually the best choice. IKEv2/IPSec is another option that is very fast and stable.
Perfect for Mobile: If you mostly use a VPN on your phone or tablet, WireGuard is a great choice because it works quickly and doesn’t use a lot of battery power. IKEv2/IPSec is also a strong candidate because it is the most stable way to switch between Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
Check the App of Your VPN Provider: Most trustworthy VPN providers offer a range of protocols. Go to the settings menu of your VPN app. A lot of providers have a “Automatic” or “Recommended” setting that picks the best protocol for your network conditions. This is good for most people, but knowing what your options are gives you more power.
Experiment and Test: Don’t be afraid to try out different VPN protocols to find the one that works best for you. Do a speed test on each one. You might find that OpenVPN (UDP) works better on your home network and IKEv2 works better on public Wi-Fi.
Stay Up to Date: VPN technology is always changing. Always make sure your VPN client software is up to date. Updates usually fix bugs, make things run better, and add security patches to the protocols.
Get Around Firewall Restrictions: In some networks with strict rules (like schools, workplaces, or countries that censor the internet), some VPN protocols might not work. When set up to use TCP port 443, OpenVPN is often the best at getting around these restrictions because it makes VPN traffic look like regular secure web browsing (HTTPS).
Read Reviews from Other Sources: Before signing up for a VPN service, look at reviews and comparisons from other sources. Websites like TechRadar, PCMag, and Comparitech are great places to find out how well the protocols offered by different providers work and how safe they are.
Use Split Tunneling: A lot of the best VPN clients have a feature called split tunneling. This lets you send only certain app traffic through the VPN while other traffic goes through your normal internet connection. For instance, you could use OpenVPN to protect your browser traffic while letting your online game connect directly to the internet for less lag.
Check Your Connection Often: Make it a habit to check that your VPN is connected and that your chosen protocol is active, especially before doing anything sensitive. A lot of VPN apps have a “kill switch” that stops all internet traffic if the VPN connection drops. This keeps data from leaking. Make sure this option is turned on.
What Will Happen to VPN Protocols in the Future
The world of VPN protocols is always changing. The rise of WireGuard has pushed the whole industry forward by focusing on speed and modern cryptography. We can look forward to more new ideas in the years to come. Researchers and developers are always coming up with new protocols and ways to make old ones better in order to make things safer, faster, and easier to use.
Looking ahead, one of the most important areas of research is the creation of quantum-resistant cryptography. As quantum computers become real, today’s encryption standards could be broken. Future VPN protocols will need to be ready to protect against this threat.
Giving You More Control Over Your Online Safety
In today’s digital age, knowing about VPN protocols is no longer just for techies; it’s an important part of being responsible online. You can make smart choices to keep your privacy and security safe if you know the pros and cons of different protocols. Choosing the right protocol gives you control over your online experience, whether you want the ironclad, clear security of OpenVPN, the lightning-fast speeds of WireGuard, or the dependable mobile connectivity of IKEv2/IPSec. A VPN is a powerful tool, and you can use it to its full potential if you know how it works. Be safe and sound out there!
Resources
For those who want to delve deeper into the world of VPN Protocols Explained, here are some valuable resources:
- “What is a VPN Protocol?” – NordVPN: https://nordvpn.com/what-is/vpn-protocol/ (Backlink to a reputable VPN provider explaining VPN protocols)
- “VPN Protocols Explained: OpenVPN, L2TP, PPTP, SSTP, IKEv2 & WireGuard” – ExpressVPN: https://www.expressvpn.com/blog/vpn-protocols-explained/ (Backlink to another leading VPN provider’s explanation)
- “WireGuard: Next Generation VPN” – WireGuard Official Website: https://www.wireguard.com/ (Source link to the official WireGuard website)
- My Previous Blog Post on Choosing the Right VPN: [Insert Link to Your Previous Relevant Blog Post Here] (Interlink to your own content)
- Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) on VPNs: https://www.eff.org/ (Source link to a leading digital rights advocacy group)
- https://bigezwehotv.rw/category/trends/